Sempra Energy
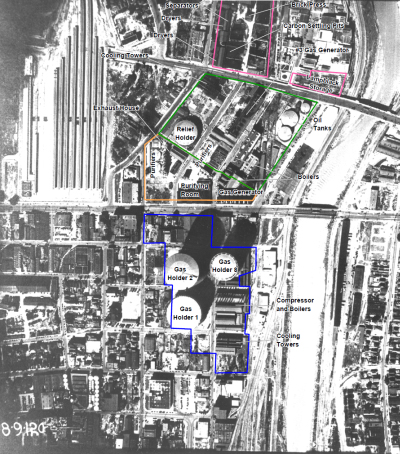
The 256-acre former Aliso Street manufactured gas plant (MGP) site is located in downtown Los Angeles. MGP operations began in 1874 and used both coal-based processes and oil-based processes. When natural gas became available in 1922, the gas plant was placed on standby. In 1942, the facilities were converted to produce butadiene, a raw material for synthetic rubber, which was operated for the US government by SCG from 1943 to 1947. Most of the facilities were demolished in 1952, except for the large gasholders and associated equipment that were removed in 1973. The property was then sold and redeveloped for other industrial and commercial activities including a gasoline and diesel fuel terminal, bus maintenance facility, metal cleaning plant, mannequin manufacturing plant and vehicle refueling centers with multiple fuel USTs.
Remedial investigations and site cleanup operations by Tetra Tech began in 1998 and continue through the present. Remediation to date has removed over 510,000 tons of soil, which eliminated over 34 tons of naphthalene, other PAHs, and VOCs. Baseline and cost-remediation risk assessments were conducted in addition to clean-up goals for soil. This work includes evaluation of groundwater data for the entire Aliso Site. Groundwater quality has been monitored on a quarterly basis since 1996 at a network of up to 122 wells. A comprehensive Groundwater Quality Management Plan was prepared that includes data evaluation, development of risk-based goals, flow and transport modeling, and review of potential remedial options. A total of 42 organic chemicals, including BTEX, MTBE, and PAHs; TPH as gasoline, diesel, and heavy hydrocarbons; and two trace metals (boron and zinc) were detected in the shallow wells. Risk-based goals were developed for industrial workers to provide protection from indoor air inhalation and drinking or contacting the groundwater. Although the groundwater is not used as source of drinking water, the data were compared to MCLs and other groundwater criteria.
Groundwater flow at the Aliso Site was modeled as a four-layer system using the USGS MODFLOW model from the ground surface to the top of bedrock. MT3D was used to simulate groundwater transport of selected organic chemicals.
Contact
Karen Summers
(925) 280-7424





